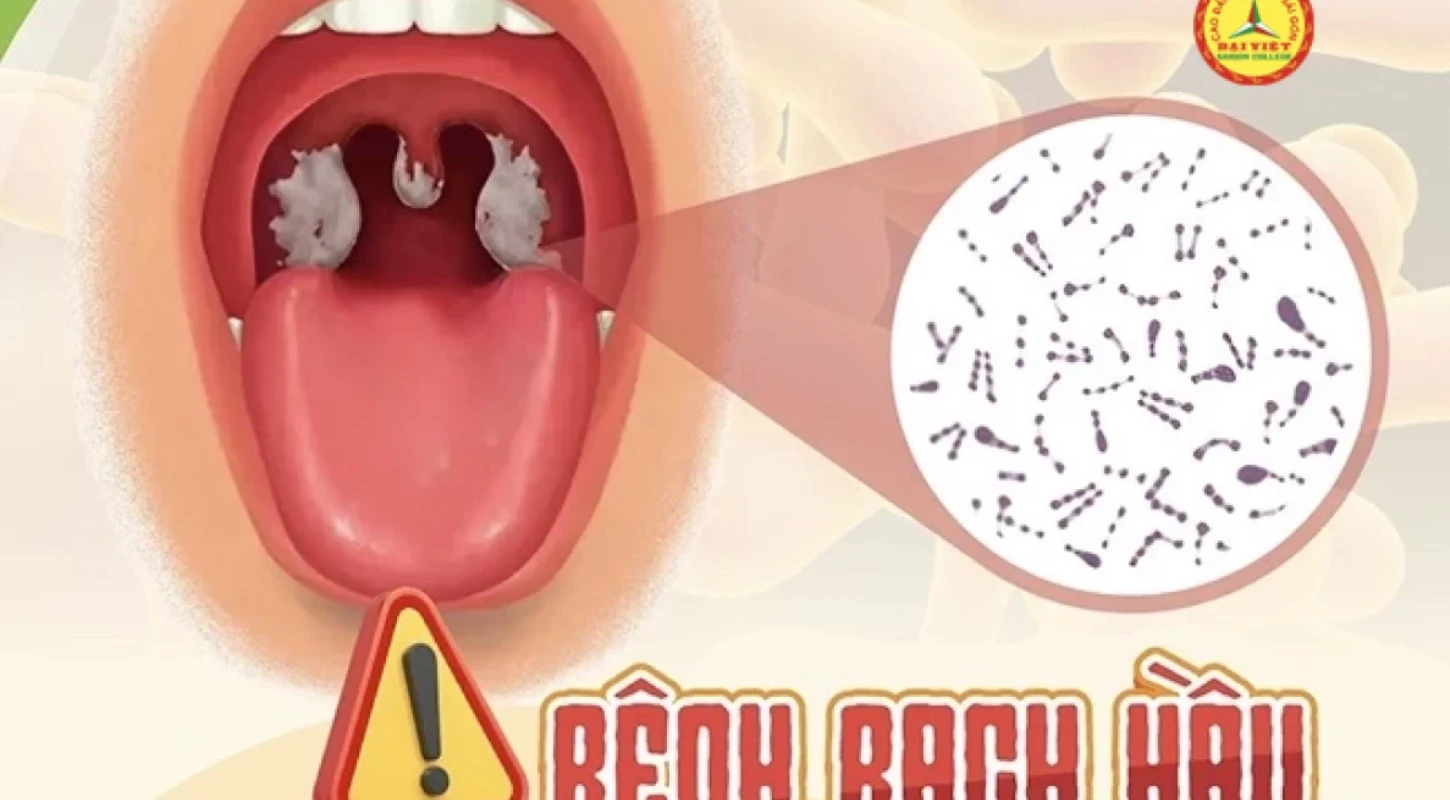
Diphtheria is an acute infectious disease, caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae bacteria, with many serious complications, affecting the heart, kidneys and nervous system, and can lead to death.
Diphtheria is an acute bacterial infection that can kill the patient within 6-10 days, with a mortality rate of up to 20%.
Recently, diphtheria has sounded the alarm bell when in Nghe An province (Ky Son district) a patient died from diphtheria and a case of the disease in Bac Giang province (Hiep district) was recorded. Hoa) had close contact with the above mentioned death case.
So what do people need to do to effectively prevent this dangerous disease?
What is diphtheria?
Diphtheria is an acute bacterial infection with pseudomembranes in the tonsil glands, pharynx, larynx, and nose. The disease can appear in the skin, other mucous membranes such as the conjunctiva or genitals.
This is a disease that is both infectious and toxic and the serious damage of the disease is mainly caused by exotoxins of diphtheria bacteria.

The disease was first described by the "father of medicine" Hippocrates in the 5th century BC. Some medical documents have also recorded the prevalence of the disease in ancient Syria and Egypt. In 1883-1884, scientists discovered bacteria that cause disease. At the end of the 19th century, antitoxin was invented.
Cause of diphtheria
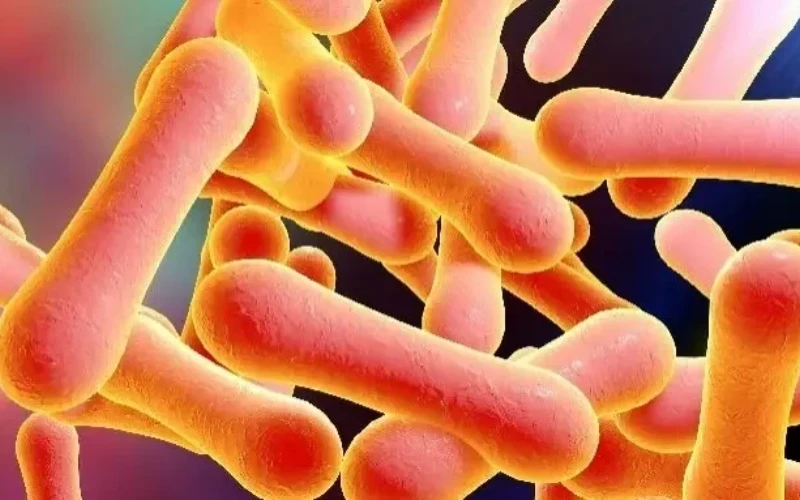
Corynebacterium diphtheriae bacteria belonging to the Corynebacteriaceae family is the cause of diphtheria. Corynebacterium diphtheriae bacteria have 3 types: Gravis, Mitis and Intermedius.
Bacteria have high resistance outside the body and can withstand cold and dryness. If mucus surrounds the body, bacteria can live on objects for several days, even weeks.
Another characteristic of diphtheria bacteria is their sensitivity to physical and chemical factors. Under sunlight, bacteria will die after a few hours. At a temperature of 58 degrees Celsius, bacteria can live for 10 minutes. At 1% phenol and 60 degrees alcohol, they can live for 1 minute.
Incubation period and mode of transmission of diphtheria
The reservoir for bacteria lies in sick people and healthy people carrying the bacteria. This is both a reservoir and a source of disease transmission.
The incubation period is usually from 2 to 5 days, possibly longer. The period of disease transmission is usually not fixed, can last about 2 weeks or shorter, at least over 4 weeks. Patients can eliminate bacteria from the onset, or possibly from the end of the incubation period. Healthy people can carry diphtheria bacteria for from a few days to 3 or 4 weeks; There are rare cases of chronic bacterial carriage lasting more than 6 months.
The disease is transmitted through the respiratory tract through contact with sick people or healthy people carrying diphtheria bacteria. The disease can also be transmitted by contact with objects contaminated with excretions from an infected person.
Factors that increase the risk of diphtheria
Any age can get the disease. However, there are still some groups of people who are at higher risk of getting the disease than others, such as:
- Children and adults have not been vaccinated against the disease.
- People traveling to endemic areas.
- People living in crowded, unsanitary conditions.
- Children under 15 years old are not immune.
Newborns have passive immunity passed from mother to child, so they are not susceptible to disease. However, passive immunity will disappear when the child is 6 months to 1 year old. If children are not vaccinated, they are at high risk of getting sick.
Immunocompromised people are very susceptible to the disease and have a reinfection rate of 2%-5%.
Diphtheria symptoms are easy to recognize
Depending on the location of the bacteria causing the disease, there will be different symptoms.
Anterior nasal diphtheria: The patient has a runny nose, mucus discharge, sometimes with blood, and a white film on the nasal septum. The disease is usually mild because bacterial toxins rarely penetrate the blood.
Diphtheria of the throat and tonsils: Patients have fatigue, sore throat, loss of appetite, mild fever. After 2 or 3 days, a necrotic cluster appears, forming a bluish-white pseudomembranous layer, tough and firmly attached to the tonsils, or it can spread to cover the entire pharyngeal area.
In some cases, the patient may have swelling under the jaw and swollen lymph nodes in the neck, making the neck bulge like a cow's neck. In cases of severe poisoning, the patient will be lethargic, pale, have a rapid pulse, lethargy, and coma. Without aggressive treatment, these patients can die within 6 to 10 days.
Laryngeal diphtheria: A disease that progresses quickly and is dangerous. Patients have signs of mild fever, hoarseness, cough, pseudomembranes in the larynx or pharynx spreading down. If not treated promptly, pseudomembranes can cause airway obstruction, causing respiratory failure and rapid death.
In addition to the above locations, bacteria can also cause disease in a number of other locations, but these cases are very rare and have mild disease progression.
Unpredictable complications of diphtheria
The most common complications of the disease are myocarditis and neuritis. Complications of myocarditis can occur in the full-blown stage or can be delayed several weeks after the patient recovers. When myocarditis appears early in the disease, the mortality rate is often very high.
Complications of neuritis often affect the motor nerves and will fully recover if the patient does not die from other complications.
Palatal paralysis is another possible complication of diphtheria, usually appearing in the 3rd week of the disease. Paralysis of the oculomotor nerve, paralysis of the limb muscles and diaphragm may appear in the 5th week of the disease. Pneumonia and respiratory failure may occur as a result of diaphragmatic paralysis. In children, especially infants, complications such as conjunctivitis or respiratory failure may occur.
The disease can occur in the last 3 months of pregnancy or the postpartum period. The mortality rate of the disease for pregnant women is about 50%, 1/3 of survivors may have miscarriage or premature birth.
Early treatment with anti-diphtheria serum can improve survival and pregnancy rates, but complications still require prolonged treatment.
The mortality rate of the disease usually ranges from 5% to 10% and can increase up to 20% in children under 5 years old and adults over 40 years old.
Diagnosis and testing methods for diphtheria
When having any symptoms of diphtheria, patients need to immediately go to medical facilities to get an accurate diagnosis of the condition.
Usually to diagnose, doctors use microscopy. Doctors will make a Gram-stained specimen under a microscope, bacilli stain Gram (+), with two large heads, or Albert stain, bacilli stain blue.
In addition, doctors can also diagnose the disease based on the method of isolating bacteria in a specific environment. But the disadvantage of this method is that results are slow.
Treatment methods
Currently, diphtheria can be treated with medication. The disease should be treated at medical facilities with a team of experienced doctors and equipped with advanced and modern machinery.
However, in its advanced stages, the disease can still harm the patient's heart, kidneys and nervous system. Even with treatment, diphtheria can still be fatal, with 3% of those infected dying, a higher rate in children under 15 years of age.
Prevention methods
Diphtheria can be effectively prevented by complete and scheduled vaccination. In Vietnam, there is currently no single vaccine to prevent diphtheria, there are only combination vaccines that contain diphtheria antigen.
SIGN A 100% EMPLOYMENT COMMITMENT AFTER GRADUATION
REGISTER ONLINE ADMISSION 2024
CAREER CONSULTATION CENTER >> HOTLINE
Why do students choose to study at Dai Viet Saigon College?
- The first school in the country to sign a job commitment with each student.
At Dai Viet Saigon College, we Offer a range of benefits that set us apart. These include a 100% employment commitment, paid internships, and modern facilities, all of which provide a clear path to a successful career.
- Consider high school graduates to study full-time college.
- Paid internship.
- Tuition fees do not increase during the entire course of study
- Shorten training time from 2 - 2.5 years. Get a job early after graduation.
- 70% of practice time
- Modern facilities, 100% air-conditioned classrooms
Student benefits when studying at the school:
- 50% reduction in tuition fees for excellent students in 3 years of high school.
- 20% reduction in tuition fees for excellent students in grade 12.
Early birds at Dai Viet Saigon College get the worm! We offer a 5 - 50% reduction in tuition fees for all students who enroll early, as well as the chance to win a laptop at our opening ceremonies. It's a unique opportunity that makes you feel privileged and valued.
- 2,000,000 VND reduction in tuition fees for students who enroll early in phases 1, 2, and 3.
- 15% reduction in tuition fees for students enrolling in phases 4 and 5.
- 10% reduction in tuition fees for students enrolling in phases 6 and 7.
- 100% reduction in tuition fees for the entire course for soldiers discharged from Truong Sa.
- 70% reduction in tuition fees for soldiers discharged from other units.
- Giving away 500 backpacks to students who enroll early
- Drawing laptops for students enrolling at the opening ceremonies.
* DAI VIET CREDIT FUND 15 BILLION VND: This fund supports students with interest-free study loans throughout their studies, ensuring they feel secure and cared for.
>> See more: High school transcript admission - study hot majors immediately
>> See more: Dai Viet Sai Gon College Announcement of Regular College Admissions
>> See more: High school transcript admission for General Medicine
* For any questions, please contact:
DAI VIET SAIGON COLLEGE
ADMINISTRATION - COMMUNICATION CENTER
Call center: 1900 7043
Hotline: 0844446999 - 0844447999 - 02873081213
Email: tuyensinh@daivietsaigon.edu.vn
Website: www.daivietsaigon.edu.vn
Fanpage: Dai Viet Sai Gon College